The most common cause is that one side of the link, typically the switch is not auto-negotiating and is set to 100 mbps full duplex and the system adapter is set to auto-negotiate. The auto-negotiation specification states that if the auto-negotiating device does not see the auto-negotiation protocol from its link peer it MUST set itself to half duplex. It can determine the correct speed because the signaling of a 10 mbps link is significantly different from the signaling of a 100 mbps link. The gigabit specification requires both sides of the link to auto-negotiate so this is not an issue on gigabit links.
This article covers how to identify and correct duplex mismatch problems for Stratus VOS STCP systems, Linux based ftServer systems and Microsoft Windows based ftServer systems.
The netstat -interface command will display low level statistics which you can use to identify a duplex mismatch. First, if the RED counters are going up the adapter is in half duplex mode. If the "Transmit frame discarded, late collisions" counter is climbing then the chances are the switch it is connected to is in full duplex mode. If all the RED counters are 0 or at least not climbing the adapter is either in full duplex mode or in half duplex mode on a link with an extremely low volume of packets. If any of the YELLOW counters are climbing the chances are that the switch is in half duplex mode while the adapter is in full duplex mode (assuming that the RED counters are not climbing). There are other reasons for these counters to be non-zero but in the vast majority of cases it is a duplex mismatch.
For a fault tolerant interface made up of two adapters the netstat command will display the statistics of the active adapter first, then the statistics of the standby adapter. To identify the actual adapter, use the dlmux_admin command with arguments of the interface name and "sdlmux_status"; it will list the adapters that are part of the interface, which one is active and what their link state is. In the following case #ENET-A-1 is the active adapter.
For PCI adapters (Continuum K470 and K480 daughter adapters and all V-series adapters including embedded adapters) you can positively check what duplex state the adapter is running at with the analyze_system request dump_genet. Match on duplex to reduce the amount of output. Notice that you have to use the adapter name and not the interface name.
For Continuum K460 adapters, the adapter's duplex setting is based on the duplex value in the parameter string of the device definition. If the duplex value is not defined it will default to half. Continuum K450 and K104 adapters will run ONLY in half duplex.
Starting with release 17 netstat will also report the duplex setting,
The simplest solution is to change the switch. This typically takes only a few commands and results in a just a momentary link drop. If changing the switch is not an option you can change the adapter.
Assuming that the interface to be changed is the sdlmux group SDLMUX-GROUP-A and the group is composed of the two adapters ENET-A-1 and ENET-A-2 you would take the following steps
The first thing you need to do is list all the Ethernet adapters. The "ftsmaint lsVnd" command will do that as well as associate those adapters to specific interfaces and associate the interfaces with an IP address. As an added bonus the command will list the speed and duplex setting of each adapter.
In the above example do not confuse the DUPLEX status in column 3 with the Ethernet duplex state. The DUPLEX status indicates that the interface or group name is made up of 2 (or more) adapters. In the above case we can see that bond0 is made up of the two adapters eth100200 and eth110200, both of which are running at 100 mbps full duplex.
Once the adapter name is know the "ethtool -S" command can be used to display low level statistics which you can use to identify a duplex mismatch. First, if the RED counters are going up the adapter is in half duplex mode. If the "tx_abort_late_coll" counter is climbing then the chances are the switch it is connected to is in full duplex mode. If all the RED counters are 0 or at least not climbing the adapter is either in full duplex mode or in half duplex mode on a link with an extremely low volume of packets. If any of the YELLOW counters are climbing the chances are that the switch is in half duplex mode while the adapter is in full duplex mode (assuming that the RED counters are not climbing). There are other reasons for these counters to be non-zero but in the vast majority of cases it is a duplex mismatch.
The ethtool command can also be used to determine if the adapter is doing auto-negotiation and if so what it is advertising.
If the switch is set to not auto-negotiate you need to set the adapter to the same speed and duplex setting as the switch. Assuming the switch is set to 100/full you can set the adapter the same why with the commands:
If the switch is set to auto-negotiate you have to set the adapter to auto-negotiate.
The advertise value of 3F tells the card to advertise all supported speeds and duplex values. You can advertise any set of values by combining the following values:
Frankly, if you are going to auto-negotiate I don't see why you would want to do anything but Auto (3F) but it's an option.
The only error counters that I have been able to find on the ftServer are the Send and Receive Errors under the Network Driver tab of the Intel PROSet display. I have found that when the adapter is running at half duplex and the switch is full duplex the "Send errors" will go up and when the adapter is set to full duplex and the switch set to half the Receive Errors will go up.
Unfortunately the Network Driver tab is not displayed in PROSet release 11 which is part of the ftServer release 5. So in release 5 of ftServer there are no statistics on the server that will indicate a duplex mismatch. You have to rely on statistics on the switch.
The Microsoft Windows "netstat -e" command does have an errors counter but while the counter sometimes goes up I have not been able to correlate it to any specific error or error condition. I do not consider it a reliable indication of anything.
To determine what duplex the adapter is running at you can look under the General tab of the Intel PROSet display for releases 4x and 9x or under the "Link Speed" tab for PROSet release 11x. Release 4x (figure 2) will have a green "LED" beside "Full Duplex" if the adapter is running at full duplex and the LED will be off (grey) if it is running at half duplex. Release 9x (figure 3) will actually say full or half duplex. Release 11x (figure 4) will also specify full or half duplex.
The Intel PROSet display also allows you to change the duplex settings. Exactly where in the display will vary depending on the release and the type of adapter (10/100 mbps versus 10/100/1000 mbps). Note that changing the settings of the adapter will cause the link to drop for a few seconds.
In the above figure note that you can configure the card to auto-negotiate any set of speeds and duplex values or not auto-negotiate and force the card to use a specific speed and duplex value. Note also that when forcing a speed your only choices are 10 or 100.
Note in figure 7 that the options are to auto-negotiate either a best speed or only 1000 mbps or to force a specific speed and duplex value. Note that the Speed tab also duplicates the Network Status display under the General tab.
One final note, prior to ftServer release 5 (PROSet release 11) the PROSet display could be brought up by double clicking on the PROSet icon in the task bar (figure 9). Starting in ftServer release 5 PROSet has been integrated into the properties dialog of the adapter displayed by the Device Manager. HOWEVER, the Link Speed tab will not be displayed if you use remote desktop to connect to the server unless you use either the /console or /admin arguments (depending on your release) on the mstsc command.
Stratus VOS STCP systems
Identifying duplex mismatch on an STCP adapter
netstat -interface #SDLMUX-GROUP-A
Ethernet adapters are grouped
Number of failovers = 3
Active Device Statistics:
MAC Type : CSMA/CD
MAC Address: 00:00:a8:42:34:b7
Device Name: #SDLMUX-GROUP-A
Line Speed : 100 mb/s
MAC Statistics:
Received frames : 40875077
Received multicast and broadcast frames : 1109935
Received octets : 3680280538
Transmitted frames : 49595968
Transmitted octets : 634292608
LAN Chipset re-initialized : 0
SQE error : 0
Transmit ring full : 0
Transmit frame discarded, late collisions: 423583
Transmit frame was deferred : 609191
Transmit frame after a single retry : 131346
Transmit frame after multiple retry : 10441
Transmit frame discarded, excessive retry: 0
Receive frame discarded, lack of buffers : 0
Receive frame discarded, improper framing: 0
Receive frame discarded, an overflow : 0
Receive frame discarded, bad CRC : 0
Receive frame discarded, bad address : 0
Receive frame discarded, congestion : 0
MAC Summary:
Transmitted frames : 49595968
Transmitted octets : 634292608
Retransmitted frames : 750978
Received frames : 41985012
Received octets : 3680280538
Total of lost frames : 0
Partner Device Statistics:
. . .
dlmux_admin #SDLMUX-GROUP-A sdlmux_status
Group Name: #SDLMUX-GROUP-A
Device Name: %phx_vos#ENET-A-1
Adapter State: ACTIVE UP
Partner: %phx_vos#ENET-A-2
Partner State: UP
as: match duplex; dump_genet ENET-A-1
Full Duplex = FULL
ForcedSpeedDuplex = 0003
as:
The Full Duplex field will either be FULL or HALF. The ForcedSpeedDuplex tells you what the adapter is fixed for. Note however that 0 can also mean auto-negotiate.
HALF_10 = 0,
FULL_10 = 1,
HALF_100 = 2,
FULL_100 = 3
Correcting duplex mismatch on an STCP adapter
The simplest thing to do for the last three steps is to look in start_stcp.cm and copy the dlmux_admin, ifconfig and route commands for the interface from the macro.
'-sdlmux #SDLMUX-GROUP-A -speed 100 -duplex full'
I am assuming here that the switch is set to 100/full. If the switch is set to auto-negotiate the parameter string would be
'-sdlmux #SDLMUX-GROUP-A'
Do not forget the single quotes surrounding all the parameters
where PARAMETERS are the ifconfig parameters and arguments used to configure the interface.Linux based ftServer systems
Identifying duplex mismatch on a Linux based ftServer adapter
# /opt/ft/bin/ftsmaint lsVnd
Virtual Network Device (VND) Groups
===================================
Group Name Status Inet Address RX Errors TX Errors Collisions
---------------------------------------------------------------------
bond0 ONLINE 172.16.1.44 0 0 0
bond1 ONLINE 10.1.1.44 0 0 0
bond2 OFFLINE - 0 0 0
bond3 OFFLINE - 0 0 0
bond4 OFFLINE - 0 0 0
VND Group Members
=================
Member Group Name Status Interface Link State Link Speed
--------------------------------------------------------------------------
eth100200 bond0 DUPLEX UP LINK 100Mb/s-FD
eth100201 bond1 SIMPLEX UP LINK 100Mb/s-FD
eth110200 bond0 DUPLEX UP LINK 100Mb/s-FD
eth110201 bond1 BROKEN UP NOLINK -
# ethtool -S eth100201
NIC statistics:
rx_packets: 912477
tx_packets: 27277
rx_bytes: 68499233
tx_bytes: 32840807
rx_broadcast: 891524
tx_broadcast: 309
rx_multicast: 7
tx_multicast: 8
rx_errors: 0
tx_errors: 8
tx_dropped: 0
multicast: 7
collisions: 9
rx_length_errors: 0
rx_over_errors: 0
rx_crc_errors: 52
rx_frame_errors: 0
rx_no_buffer_count: 0
rx_missed_errors: 0
tx_aborted_errors: 0
tx_carrier_errors: 0
tx_fifo_errors: 0
tx_heartbeat_errors: 0
tx_window_errors: 8
tx_abort_late_coll: 8
tx_deferred_ok: 10
tx_single_coll_ok: 7
tx_multi_coll_ok: 1
tx_timeout_count: 0
tx_restart_queue: 0
rx_long_length_errors: 0
rx_short_length_errors: 0
rx_align_errors: 0
tx_tcp_seg_good: 0
tx_tcp_seg_failed: 0
rx_flow_control_xon: 0
rx_flow_control_xoff: 0
tx_flow_control_xon: 0
tx_flow_control_xoff: 0
rx_long_byte_count: 68499233
rx_csum_offload_good: 23045
rx_csum_offload_errors: 0
rx_header_split: 0
alloc_rx_buff_failed: 0
tx_smbus: 0
rx_smbus: 0
dropped_smbus: 0
#ethtool eth100201
Settings for eth100201:
Supported ports: [ TP ]
Supported link modes: 10baseT/Half 10baseT/Full
100baseT/Half 100baseT/Full
1000baseT/Full
Supports auto-negotiation: Yes
Advertised link modes: 10baseT/Half 10baseT/Full
100baseT/Half 100baseT/Full
1000baseT/Full
Advertised auto-negotiation: Yes
Speed: 100Mb/s
Duplex: Half
Port: Twisted Pair
PHYAD: 0
Transceiver: internal
Auto-negotiation: on
Supports Wake-on: d
Wake-on: d
Current message level: 0x00000007 (7)
Link detected: yes
Correcting duplex mismatch on a Linux based ftServer adapter
# ethtool -s eth100201 autoneg off
# ethtool -s eth100201 speed 100
# ethtool -s eth100201 duplex full
# ethtool -s eth100201 autoneg on
# ethtool -s eth100201 advertise 0x3F
0x001 10 Half
0x002 10 Full
0x004 100 Half
0x008 100 Full
0x020 1000 Full
0x800 10000 Full
0x03F Auto
Microsoft Windows based ftServer systems
Identifying duplex mismatch on a Microsoft Windows based ftServer adapter
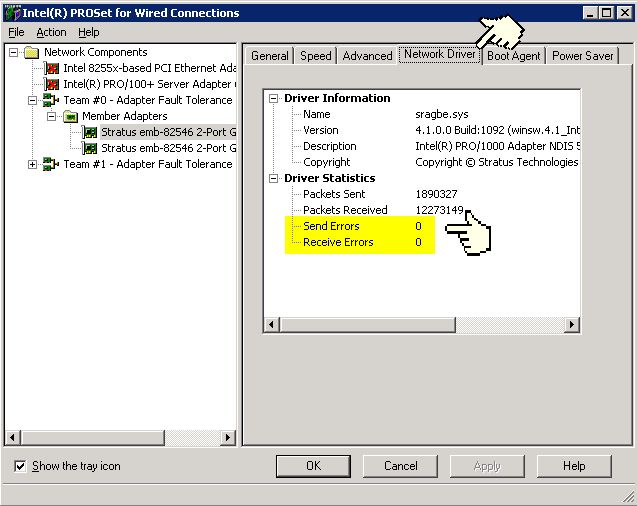
Figure 1 - Intel PROSet Network Driver Tab
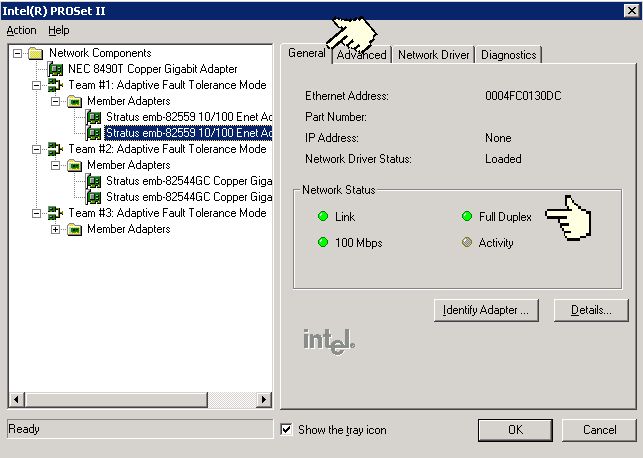
Figure 2 - Intel PROSet 4x General Tab
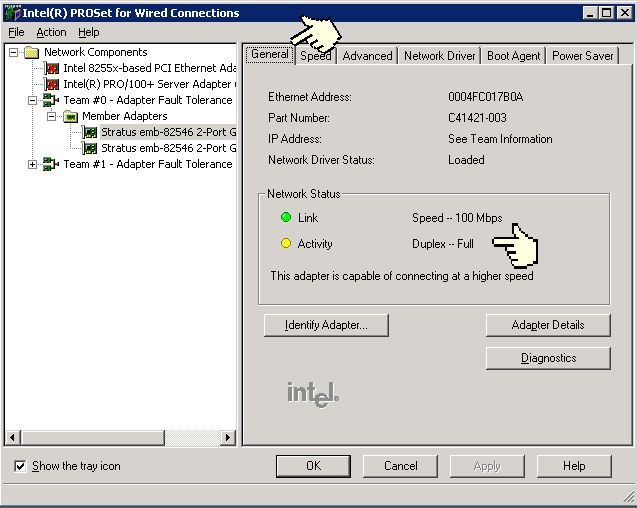
Figure 3 - Intel PROSet 9x General Tab
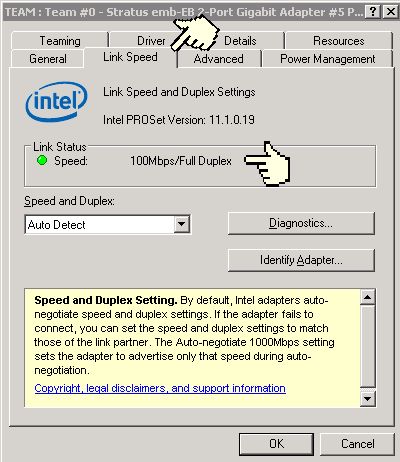
Figure 4 - Intel PROSet 11x Link Speed Tab
Correcting duplex mismatch on a Microsoft Windows based ftServer adapter
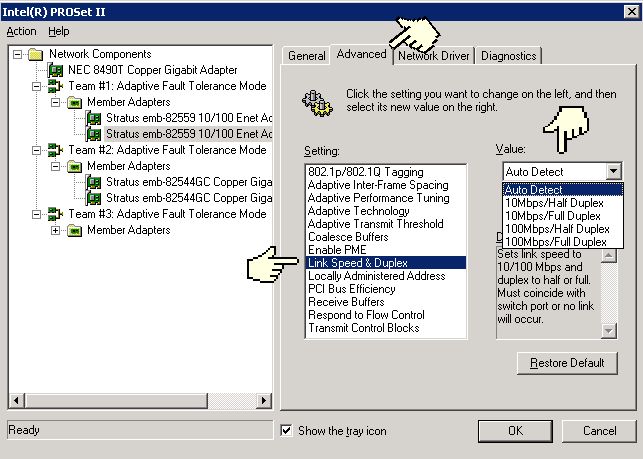
Figure 5 - Intel PROSet release 4x Advanced tab for 10/100 adapters
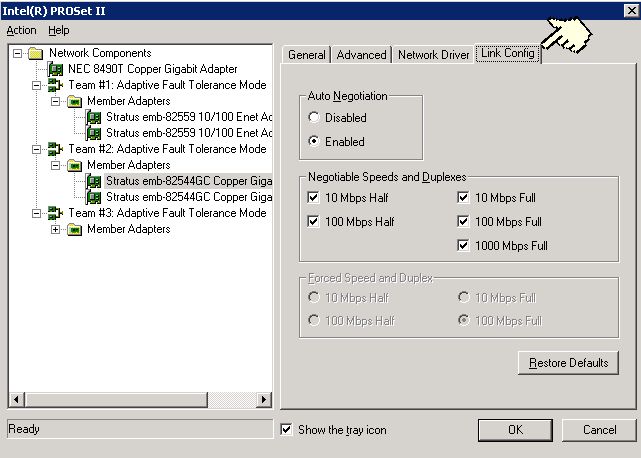
Figure 6 - Intel PROSet release 4x Link Config tab for 10/100/1000 adapters
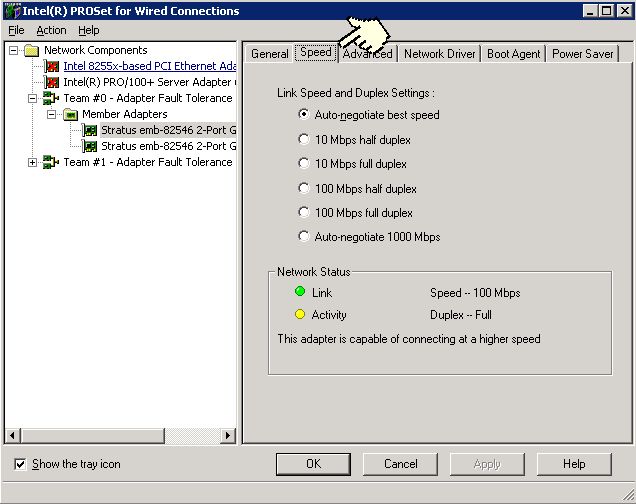
Figure 7 - Intel PROSet release 9x Speed tab
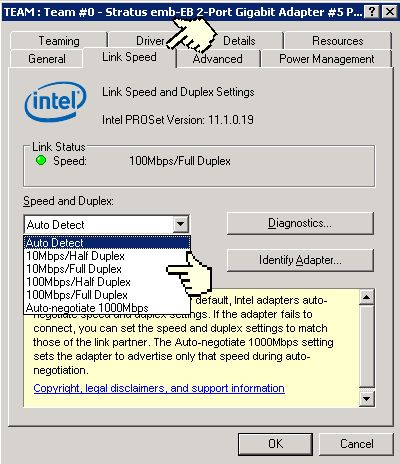
Figure 8 - Intel PROSet release 11x Link Speed tab
Figure 9 - Intel PROSet 4x and 9x icon on the task bar
![]()
This page was last modified on 08-08-27![]() Send comments and suggestions
Send comments and suggestions
to ndav1@cox.net