| Proper Switch Configuration for Trouble-Free Ethernet Operation of VOS Modules |
Noah Davids
Stratus Support Engineer
Stratus Technologies
Proper Switch Configuration for Trouble-Free
Ethernet Operation of VOS Modules
For the proper functioning of your VOS Ethernet adapters and optimal performance of your TCP/IP communication, it is not enough that the Stratus configuration be correct. Your Ethernet switch configuration must also be correct. An incorrectly configured switch can result in degraded or unacceptable TCP performance or even complete communication failure. To make matters worse, the problem might not be noticed until there is a failover due to the failure of the active adapter. This article will discuss the proper configuration of the switch ports connected to Stratus® VOS adapters.
The number of models and brands of switches makes it impossible to discuss specifics of every model. Instead, I will describe the configuration for a Cisco® Catalyst® 6500 Series Switch. It is quite possible that your switch uses the same features and commands; if not your network administrator will have to ask your switch vendor what the equivalent commands are.
The switch ports that connect to adapters that are dlmux or sdlmux partners must be configured the same. Many network administrators do not realize that there are two adapters with the same IP address. They configure the switch port for the active adapter, test with a ping and leave it at that. The standby adapter is left with all the default settings. The result is that things work fine until there is a failover, then nothing works.
I strongly recommend that you go over the switch settings with your network administrator to confirm that they are set correctly. I also recommend that you schedule a monthly failover test. I have found that settings on switch ports have a mysterious way of changing. The test can be done simply by starting a ping from another host to the Stratus, pulling the cable out of the active adapter and confirming that the pings are still receiving a response. You will probably loose one ping, you may loose two, but anything more than four presents a problem that should be investigated. It is also possible for all pings to fail if the switch port connected to the standby adapter has become miss-configured, so plan the time of the test when a communication outage will not present a problem, or at least will present a problem you can live with.
You can determine the active adapter using the dlmux_admin command. For example:
dlmux_admin #sdlmuxB.m15.12.2 sdlmux_status
Group Name: #sdlmuxB.m15.12.2
Device Name: %phx_vos#enet.m15.12.2
Adapter State: ACTIVE UP
Partner: %phx_vos#enet.m15.13.2
Partner State: UP
Shows that #enet.m15.12.2 is the active adapter.
There are six critical settings: VLAN, speed, duplex, portfast, security and inline power. Parameters for trunking, channel and dot1q tunneling should also be set.
VLAN:
VLANs are a mechanism that allows a switch to carry traffic for multiple LAN segments and to keep the traffic for those segments separated. Both adapters of a dlmux/sdlmux partnership must be on the same VLAN.
To check the VLAN numbers, use the “show port status” command.
Console> show port status 2/1
Port Name Status Vlan Duplex Speed Type
----- ------------------ ---------- ---------- ------ ------ ------------
2/1 connected 52 half 100 100BaseTX
Console> show port status 4/1
Port Name Status Vlan Duplex Speed Type
----- ------------------ ---------- ---------- ------ ------ ------------
4/1 connected 52 half 100 100BaseTX
Speed:
Ports on blades supported by the Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series can be set to 10/100 or auto. Some blades also support a speed of 1000. Auto allows the speed to be negotiated to any supported speed.
The K104, K450 and U713 do not support negotiation. If a switch port is connected to one of these adapters and the speed is set to auto, the switch will attempt to sense the speed setting of the adapter. If the switch port is set to a specific speed, then that speed is used, regardless of the speed the Stratus adapter is using. The K104 and K450 only operate at 10 mbps. As long as the switch is set to 10 or auto, the link will work as expected. The K460 does support negotiation. If a speed is listed as a parameter, only that speed is negotiated. If no speed is specified, a default of 10 mbps is used. As long as the switch port is configured to auto or the same speed as the K460, the link will come up at the desired speed.
The U713 will operate at 10 or 100 mbps, and it will also try to sense the speed of the switch port. When two devices both try to sense at which speed the other is operating, they will almost always end up using 10 mbps. This will happen even if you have a “-speed 100” as a parameter in the U713 configuration. This is a known hardware bug that cannot be fixed (rns-187). As a result a switch port connected to a U713 should always have its speed set to 100, if that is the desired speed. However, setting the switch port speed to 100 mbps on Cisco 6500 blades WS-X6548-RJ-45 blade and WS-X6148-RJ-45 may result in a failure to link between the switch port and the U713. For the WS-X6548-RJ-45 blade disabling the auto-mdix feature should correct the problem (but make sure you are using a straight through cable). The following commands can be used to disable auto-mdix and display the current state
set port auto-mdix mod/port disablewhere mod/port is the module and port that the U713 is connected to.
Example:
Console> (enable) set port auto-mdix 5/40 disable
Auto-mdix is disabled on port 5/40.To show the state use
show port auto-mdix mod/portExample:
Console> (enable) show port auto-mdix 5/47
Port auto-mdix
----- ---------
5/47 disableFor the WS-X6148-RJ-45 if you are running a release prior to 8.5(1) you must set the speed for 10 or auto to get a reliable link. Setting the speed at 100 will sometimes get you a link of 100 mbps but most of the time result in no link. If you are runing 8.5(1) or later you must set inlinepower to off (see inlinepower below).
In release 15.0 you cannot set the speed on any of the adapters on a Stratus ftServer® V Series system. This is documented as bug gbe-76 for the U577 and gbe-88 for the U575. All of the V Series adapters support negotiation. If, for some reason, you want to run at a speed lower than the maximum possible between switch and adapter, you must set the speed on the switch.
You can see what speed the switch ports are connected at with the show port status command.
Console> show port status 2/1
Port Name Status Vlan Duplex Speed Type
----- ------------------ ---------- ---------- ------ ------ ------------
2/1 connected 52 half 100 100BaseTX
Console> show port status 4/1
Port Name Status Vlan Duplex Speed Type
----- ------------------ ---------- ---------- ------ ------ ------------
4/1 connected 52 half 100 100BaseTX
The default setting is auto. This should be OK for all adapters except the U713 (assuming you want to run at 100 mbps). There is some Cisco documentation that says that you should always set an explicit speed for ports connected to servers. The documentation is not consistent, so I can’t say that this is a hard and fast rule. Still, always setting the speed instead of relying on auto will not hurt – provided the switch port and the adapter are consistent. To set the speed use the “set port speed” command
Note that gbe-76 is fixed starting with release 15.1 and gbe-88 is fixed starting in release 15.1.1aa.
Duplex:
Ports on blades supported by the Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series can be set to half, full, or auto. Auto allows the duplex mode to be negotiated to any supported mode. If the Stratus adapter does not support negotiation (K104, K450, U713), and the switch port is set to auto, it will default to half duplex mode. This is OK for the K104 and K450, but you can configure the U713 into full duplex mode. If you do set the U713 into full duplex mode, the switch port must also be set to full duplex. The K460 will default to half if you do not explicitly set the mode with the “-duplex” parameter.
As I said above, the K460 always tries to negotiate its settings, but if the switch does not negotiate a duplex mode, the K460 will still use the mode set in the parameters. Therefore, the switch port should be set to auto or the same mode as the K460. If the modes are different between the K460 and the switch port, the link will come up, but will have a duplex mismatch.
All the ftServer V Series adapters support full duplex, but again, because of gbe-76 and gbe-88, you maynot be able to explicitly set the duplex mode. This means that if you set the switch port to full duplex, the Stratus adapter will not see the switch negotiate a duplex mode and will set itself to half duplex. If you leave the switch port set to auto, both the Stratus adapter and the switch port will negotiate to full duplex. If you want to run at half duplex, you must set the switch port to half duplex or make sure that you are running a release that has these bug fixes.
All fiber gigabit adapters run in full duplex, and all copper adapters running at gigabit speeds run in full duplex mode by default. This mode cannot be changed.
You can see what duplex the switch ports are connected at with the show port status command.
Console> show port status 2/1
Port Name Status Vlan Duplex Speed Type
----- ------------------ ---------- ---------- ------ ------ ------------
2/1 connected 52 half 100 100BaseTX
A duplex mismatch will not prevent the link from working and may not even be noticeable at low frame rates. However, as the frame rate increases, there will be an increasing number of errors on the link until the point where throughput becomes a significant problem. The full duplex side of the mismatch will see Align-Err and FCS-Err errors. The half duplex side of the mismatch will have Late-Coll and Excess-Coll errors. You can see errors on the switch with the show port command.
Console> show port 2/1
Port Name Status Vlan Duplex Speed Type
----- -------------------- ---------- ---------- ------ ----- ------------
2/1 notconnect 1 full 1000 No Connector
Port Security Violation Shutdown-Time Age-Time Max-Addr Trap IfIndex
----- -------- --------- ------------- -------- -------- -------- -------
2/1 disabled shutdown 0 0 1 disabled 3
Port Num-Addr Secure-Src-Addr Age-Left Last-Src-Addr Shutdown/Time-Left
----- -------- ----------------- -------- ----------------- ------------------
2/1 0 - - - - -
Port Broadcast-Limit Multicast Unicast Total-Drop Action
-------- --------------- --------- ------- -------------------- ------------
2/1 - - - 0 drop-packets
Port Send FlowControl Receive FlowControl RxPause TxPause
admin oper admin oper
----- -------- -------- --------- --------- ---------- ----------
2/1 desired off off off 0 0
Port Status Channel Admin Ch
Mode Group Id
----- ---------- -------------------- ----- -----
2/1 notconnect auto silent 41 0
Port Status ErrDisable Reason Port ErrDisableTimeout Action on Timeout
---- ---------- ------------------- ---------------------- -----------------
2/1 notconnect - Enable No Change
Port Align-Err FCS-Err Xmit-Err Rcv-Err UnderSize
----- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------
2/1 0 0 0 0 0
Port Single-Col Multi-Coll Late-Coll Excess-Col Carri-Sen Runts Giants
----- ---------- ---------- ---------- ---------- --------- --------- ---------
2/1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0
Port Last-Time-Cleared
----- --------------------------
2/1 Tue Mar 5 2002, 11:43:01
On VOS, the “netstat –interface” command (for STCP interfaces) or the “netstat –detail command (for TCP_OS interfaces) will show you the error counters. The full duplex side will see “improper framing” or “bad CRC” errors. The half duplex side will see “late collisions” and “excessive retry” errors.
netstat -interface #sdlmux.14.2
MAC Type : CSMA/CD
MAC Address: 00:00:a8:c1:86:a1
Device Name: #sdlmux.14.2
Line Speed : 10 mb/s
MAC Statistics:
Received frames : 376944
Received multicast and broadcast frames : 376944
Received octets : 61736486
Transmitted frames : 1
Transmitted octets : 42
LAN Chipset re-initialized : 0
SQE error : 0
Transmit ring full : 0
Transmit frame discarded, late collisions: 8
Transmit frame was deferred : 8
Transmit frame after a single retry : 0
Transmit frame after multiple retry : 0
Transmit frame discarded, excessive retry: 8
Receive frame discarded, lack of buffers : 0
Receive frame discarded, improper framing: 0
Receive frame discarded, an overflow : 0
Receive frame discarded, bad CRC : 0
Receive frame discarded, bad address : 0
Receive frame discarded, congestion : 0
MAC Summary:
Transmitted frames : 1
Transmitted octets : 42
Retransmitted frames : 8
Received frames : 753888
Received octets : 61736486
Total of lost frames : 0
The default setting on a Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series is auto. This should be OK for all adapters except the U713 (assuming you want to run in full duplex). There is some Cisco documentation that says that you should always set an explicit duplex for ports connected to servers. The documentation is not consistent so I can’t say that this is a hard and fast rule. Still, as long as the switch port is not connecting to a V Series adapter setting, the duplex, instead of relying on auto, will not hurt - provided the switch port and the adapter are consistent. To set the duplex mode, use the “set port duplex” command.
Portfast:
The portfast setting allows a port to skip the listening and learning stages of the Spanning Tree algorithm. This will significantly speed up the transmission of frames after a failover.
To check the portfast setting use the “show port spantree” command.
Console> (enable) show port spantree 2/1
Port(s) Vlan Port-State Cost Prio Portfast Channel_id
------------------------ ---- ------------- --------- ---- -------- ----------
2/1 1 connected 2684354 32 enabled 0
By default, portfast is disabled, so it must be enabled. To enable portfast you can use either the “set spantree portfast” command or the “set port host” command.
Security:
The security setting allows you to specify what addresses can be attached to the port and what the effects of an address violation will be. To check on the security setting, use the “show port security” command.
You either want security disabled, or you want to specify the MAC addresses of both the primary and secondary adapters. Remember, the addresses differ only by one bit in the fourth octet, so you have to look closely to distinguish the two.
Console> (enable) show port security 2/1
Port Security Violation Shutdown-Time Age-Time Maximum-Addrs Trap IfIndex
----- -------- --------- ------------- -------- ------------- -------- -------
2/1 enabled shutdown 120 1440 25 disabled 3
Port Secure-Src-Addrs Age-Left Last-Src-Addr Shutdown Shutdown-Time-Left
---- ----------------- -------- ----------------- -------- ------------------
2/1 00-00-a8-40-3b-6e 4 00-11-22-33-44-55 No -
00-00-a8-60-3b-6e 100
Security by default is off. With any luck, you will not have to request any changes from your network administrator.
Inline Power:
Inline power is a mechanism that allows the switch port to deliver low voltage power to the device connected to it. It is used primarily for cameras and phones, but the number of devices that can make use of it is expanding. The delivery of power is negotiated when the device is connected. Theoretically, a device that does not use inline power should not be affected in any way. However, there have been a number of very difficult link establishment problems on the K460 and U713 that were resolved when the inline power setting was changed from auto to off. As a result, Stratus recommends that the inline power setting always be set to off.
The “show port inlinepower” command can be used to show the current status. You want the Admin and Oper values to be off.
Console> show port inlinepower 2/1
Default Inline Power allocation per port: 9.500 Watts (0.22 Amps @42V)
Total inline power drawn by module 3: 0 Watt
Port InlinePowered PowerAllocated
Admin Oper Detected mWatt mA @42V
----- ----- ------ -------- ----- --------
2/1 off off no 00.00 0.000
If the switch port does not support inlinepower, you will get a “feature not supported” error.
The default setting is auto. This will have to be changed on ports that support this feature. To change the setting, use the “set port inlinepower” command.
Trunking:
Trunking is negotiated when a link is established. Since Stratus adapters will not be part of a trunk, the negotiation will fail. There is no reason to delay link establishment while the switch port tries to negotiate trunking so it should be turned off.
To check the state of trunking use the “show port trunk” command. The state should be set to not-trunking.
Console> (enable) show port trunk 2/1
* - indicates vtp domain mismatch
Port Mode Encapsulation Status Native vlan
-------- ----------- ------------- ------------ -----------
2/1 off dot1q not-trunking 1
By default, trunking is on so it must be turned off. To turn trunking, off you can use either the “set trunk” command or the “set port host” command.
Channel:
The channel setting controls the protocol that is used to negotiate an EtherChannel group when the link comes up. Again, since Stratus VOS adapters will not be part of an EtherChannel group, the negotiation will fail. There is no reason to delay link establishment while the switch port tries to negotiate an EtherChannel so it should be turned off.
You can show the channel state with the “show port channel” command. The mode should be off.
Console> show port channel 2/1
Port Status Channel Admin Ch
Mode Group Id
----- ---------- --------- ----- -----
2/1 connected off 195 769
By default, channel is set to auto so it must be turned off. To turn off channel, you can use either the “set port channel” command or the “set port host” command.
Dot1q tunneling:
802.1q is another way of constructing VLANs. It is probably possible to make this feature work, however, Cisco recommends that it be disabled on ports connected to end stations. I’m not going to contradict Cisco, so for ports connected to Stratus adapters this feature should be disabled.
You can see the current status with the “show port dot1qtunnel” command.
Console> (enable) show port dot1qtunnel 2/1
Port Dot1q tunnel mode
----- -----------------
2/1 disabled
The default for this feature is disabled. If for some reason it is enabled, it can be disabled with the “set port dot1qtunel” command or the “set port host” command.
Summary of commands and status:
| Command | Expected Value |
| show port status | VLAN, speed, duplex For ports connected to a K104 or K450, speed can be auto or 10 For ports connected to a K460, speed can be auto or same speed as K460 For ports connected to U713, speed should be desired speed For ports connected to a V Series adapter, speed should be auto or desired speed For ports connected to a K104 or K450, duplex mode can be auto or half. Do not use full, it is not supported by the adapters For ports connected to a K460, duplex mode can be auto or same mode as the K460 For ports connected to U713, duplex mode should be same mode as U713 For ports connected to V Series adapter, duplex mode should be auto or half. Do not set full, setting auto will result in full duplex being set correctly |
| show port spantree | Portfast should be enabled |
| show port security | Enabled with both active and standby addresses or disabled |
| show port inlinepower | Off or “feature not supported” |
| show port trunk | Not-trunking |
| show port channel | Off |
| show port dot1qtunnel | Disabled |
The question of multiple switches:
The following discussion applies only when using dlmux devices (K104, K450 or K460) or when using sdlmux devices (U713, U714, U570, U571, U574, U575, U576, U577) on releases that do not have the sdlmux-129 fix. sdlmux-129 is fixed in 15.0.1ag and all 15.1 and 15.2 releases. There should be no problems using sdlmux devices in multiple switch topologies in releases containing the sdlmux-129 fix.
Finally, there is the question of whether it is better to have both partners plugged into the same switch or whether each partner should be plugged into a different switch. The advantage of multiple switches is increased reliability. If a switch fails, the other switch can take over.
There are however some disadvantages in using multiple switches, depending upon the topology of the network and whether you are using adapters that use dlmux (K104, K450, K460) or sdlmux (U713, U714, U570, U571, U574, U575, U576, U577).
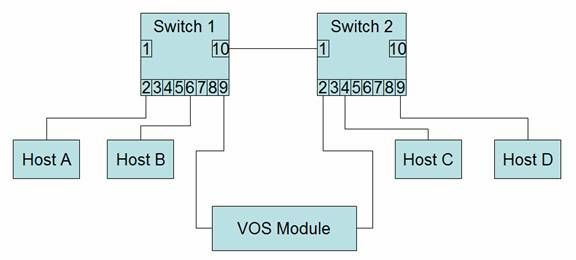
Figure 1 – simple topology
Before continuing, let’s assume that the currently active adapter is on the right side of the module and is connected to switch 2. The standby then is on the left side and connected to switch 1. Also assume that the adapters are using sdlmux. If you looked at the address mappings on switch 1 it would show:
| Port | "Address" |
| 2 | Host A |
| 6 | Host B |
| 9 | VOS module standby |
| 10 | VOS module active Host C,D |
Switch 2 address map
| Port | "Address" |
| 1 | VOS module standby Host A, B |
| 2 | VOS module active |
| 4 | Host C |
| 9 | Host D |
Now assume that the active adapter fails. The newly active adapter sends out a test message, addressed to the standby adapter, and the switch tables now show:
| Port | "Address" |
| 2 | Host A |
| 6 | Host B |
| 9 | VOS module standby VOS module active |
| 10 | Host C,D |
Switch 2 address map
| Port | "Address" |
| 1 | VOS module standby VOS module active Host A, B |
| 2 | empty |
| 4 | Host C |
| 9 | Host D |
The active MAC addresses moves to port 9 of switch 1. Note that because the test message that is sent out is addressed to the standby address, switch 2 never sees it. When host C or D sends a frame to the VOS module, switch 2 must flood the frame out all ports because it no longer has a mapping for “VOS module active”. Once VOS replies, the address is mapped to port 1.
Figure 2 shows a more complex topology with the two switches connected to a backbone switch, which also has connections to other hosts.
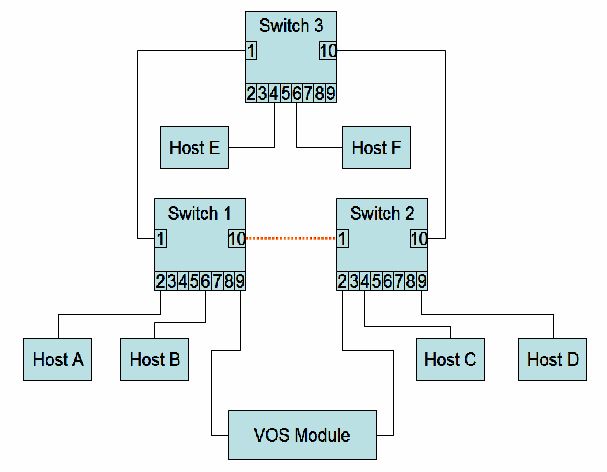
Figure 2 – more complex topology
The situation is different in figure 2. In this scenario, the link between switch 1 port 10 and switch 2 port 1 has been disabled by spanning tree to prevent loops. Before the adapter failure, the address mapping looks like this:
| Port | "Address" |
| 1 | VOS module active Host C, D, E, F |
| 2 | Host A |
| 6 | Host B |
| 9 | VOS module standby |
Switch 2 address map
| Port | "Address" |
| 2 | VOS module active |
| 4 | Host C |
| 9 | Host D |
| 10 | VOS module standby Host A, B, E, F |
Switch 3 address map
| Port | "Address" |
| 1 | VOS module standby Host A, B |
| 4 | Host E |
| 6 | Host F |
| 10 | VOS module active Host C, D |
After the failure of the active adapter and the transmission of the test packet out of the newly active adapter, we have:
| Port | "Address" |
| 1 | Host C, D, E, F |
| 2 | Host A |
| 6 | Host B |
| 9 | VOS module standby VOS module active |
Switch 2 address map
| Port | "Address" |
| 2 | empty |
| 4 | Host C |
| 9 | Host D |
| 10 | VOS module standby Host A, B, E, F |
Switch 3 address map
| Port | "Address" |
| 1 | VOS module standby Host A, B |
| 4 | Host E |
| 6 | Host F |
| 10 | VOS module active Host C, D |
Note that the address map of switch 3 has not changed. This is because the test message that was sent by the newly active adapter was never broadcast to the other switches. If either of hosts, E or F, sends a frame to the VOS module, it will be sent out of port 10 of switch 3. Switch 2 will flood it to all its other ports, but it will not get to switch 1 (remember that switch 2 port 1 has been disabled to prevent loops). If hosts C or D send a frame to the VOS module, switch 2 will flood it out all ports, including port 10, but switch 3 will inspect its address cache. Since the destination address is on the same port, it will just drop the frame. As a result, only hosts on switch 1 can communicate with the VOS module, at least until the switch 3 ages out the address entry for “VOS module active” on port 10.
If either one of the other links between the switches had been disabled by spanning tree instead of the link between switch 1 and 2, then things would have worked correctly. Of course, unless the network administrator explicitly set up link costs to control which link was disabled, it is pretty much random and the more complex the topology, the more chances that at least some hosts will lose connectivity to the module after a failover, at least until the addresses have aged out.
If the adapters use dlmux, there is a slightly different story. The message that is sent after a failover for dlmux adapters is addressed to itself, that is, both the source and destination addresses are the MAC address of the active adapter. For the figure 1 topology, this difference in message destination doesn’t matter. For the figure 2 topology, it *may* matter, depending on how the switch works. If the switch looks up the outgoing port before updating its address table, the switch will forward the frame to the other switches, and all switches will update their address tables with the new address configuration. If however, the switch updates its address table before looking up the outgoing port, it will not forward the frame and none of the other switches will update their tables. Frankly, I am not sure how the Cisco Catalyst 6500 Series does it.
My recommendation is to connect both adapters to the same switch unless you have the topology shown in figure 1.
| Originally published in Vol 6 (Dec 2004) of the Stratus eCustomer/ePartner Newsletter | ||
| Updated 05-08-30 to include information regarding link issues between the U713 and certain Cisco 6500 blades | ||
| Updated 05-11-02 to include information about gbe-88 and what releases contain the fixes to gbe-76 and gbe-88 | ||
| Updated 05-11-07 to include releases containing fix for sdlmux-129 |
Specifications and descriptions are summary in nature and subject to change without notice
Stratus and ftServer are registered trademarks of Stratus Technologies Bermuda Ltd.
Catalyst and Cisco are registered trademarks or trademarks of Cisco Systems, Inc. and/or its affiliates in the U.S. and certain other countries. All other trademarks and registered trademarks are property of their respective holders.